Why do some children develop severe allergies or autoimmune disorders when their parents have no history of either condition?
 Rather than looking to genetics for clues, the answer may lie in the communication that occurs between the T cells of the immune system and the bacteria in the gut, particularly at a very young age.
Rather than looking to genetics for clues, the answer may lie in the communication that occurs between the T cells of the immune system and the bacteria in the gut, particularly at a very young age.
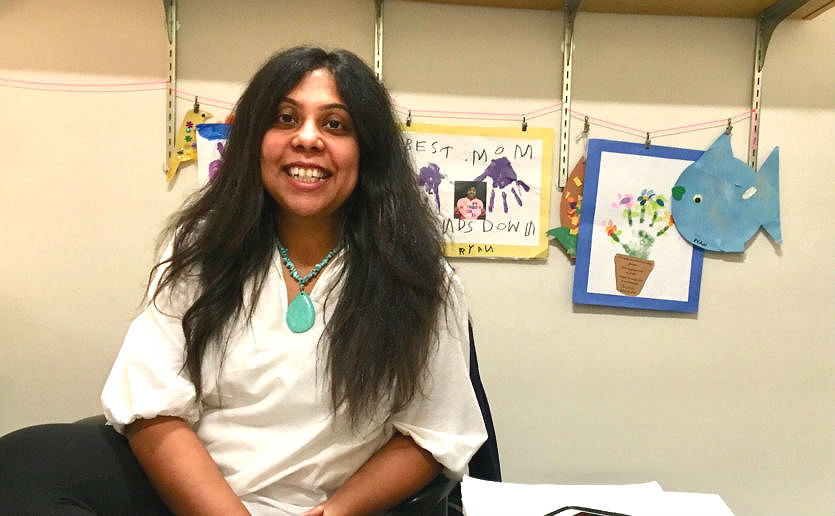
Nitya Jain, PhD, a researcher at the MassGeneral Hospital for Children’s Mucosal Immunology and Biology Research Center, is studying how changes in the bacterial population in the gut influence T cell development and how signals between the two systems drive this process.
It’s a quest that combines Dr. Jain’s longstanding scientific curiosity about T cell biology with her personal experiences as the aunt of a girl with severe allergies.
You can think of T cells as the special operations unit of your body’s immune system.
An Elite Defense Team
You can think of T cells as the special operations unit of your body’s immune system. These highly specialized cells are trained to detect and respond to harmful substances in the body, either by attacking these substances themselves, or by using chemical signals to direct other cells to attack. T cells also help to protect the healthy cells in the body by stopping other immune cells from attacking them.
T cells receive their basic training in the thymus, a small organ near the heart, shortly after birth. During this training period, the cells learn how to tell a friend from a foe.
In the case of allergies and autoimmune disorders, some signals get crossed during this T cell training, and substances or cells that are typically harmless are categorized as harmful.
Communication Challenges
Researchers have found that this signal crossing may result from alterations in the composition of bacteria in the gut. Many factors can affect this bacterial population, including the method of birth (natural vs. C-section), whether the baby is formula-fed or breast-fed, if the baby is administered antibiotics early on, and the environment in which the baby is raised.
“It’s clear that the composition of the microbiota affects how the immune cells are trained and what they respond to, but we still do not know how this communication takes place,” Dr. Jain says.
“Are there cells physically moving from the intestine to the thymus and informing the cells to develop in a particular way? Or is there a metabolite (a product of metabolism) made by the microbiota that influences what happens in the thymus?”
To learn more, Dr. Jain is studying mouse models that have not been naturally colonized by bacteria (germ-free mice), and then observing the changes in T cell development after reintroducing bacterial strains of interest.
“We have to go about this in an intelligent way,” she says. “Can we narrow down our targets by profiling the microbiota of children with celiac disease or type 1 diabetes, identifying what is different from a so-called ‘healthy’ microbiome, and use that information to guide experiments in the lab?”
The Personal Connection
An interesting new avenue of research opened up for Dr. Jain last summer when her niece came to visit her Massachusetts home. Because her niece, who lives in Singapore, has severe allergies to berries, cow’s milk and grass, Dr. Jain asked her sister (the girl’s mother) to see what allergy medication she should have on hand for the visit.
Surprisingly, her sister told her not to worry. The family had found a way to preempt the niece’s allergic reactions by giving her a probiotic — live bacteria in pill form — before exposing her to allergens.
The insights from her research could help to create new treatments for patients down the line.
During the visit, Jain watched as her niece was able to eat pizza without reacting to the lactose in the cheese and play in the yard with her two boys after she had taken a probiotic earlier in the day.
That sparked a new question for Dr. Jain. How were the bacteria in the probiotic able to stop her niece’s immune system from launching an established allergic response?
“It works, we just don’t know how,” she says. “Figuring that out will help us make better treatments, and identify other conditions where a probiotic could prevent a similar immune reaction.”
Future Treatment Options
While Dr. Jain and her team are still at the beginning stages of understanding the connections between bacteria and T cell development, the insights from her research could help to create new treatments for patients down the line.
“We’re a basic science lab. But once we figure out the influencers of early T cell development, I think our research could be applied to so many different avenues, including cancer, allergies and autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes and inflammatory bowel disease.”
To learn more about how you can support MassGeneral Hospital for Children, please contact us.